Recommended Action The following steps are suggested when
this symptom is encountered:
-
Step 1 Enable the debug lapb privileged EXEC command.
If the LAPB protocol seems stable, disable the debug lapb command
and enable the debug x25 events privileged EXEC command.
-
Step 2 Look for restarts or RESTART messages or CLEAR REQUESTS
with non-zero cause codes.
-
Step 3 To interpret the X.25 cause and diagnostic codes
provided by the output, see the "X.25 Cause and Diagnostic Codes" appendix
in the Debug Command Reference manual.
-
Step 4 Verify that the critical LAPB parameters (modulo,
T1, N1, N2 and k) and the critical X.25 parameters (modulo, X.121 address,
SVC ranges, default window and packet sizes and PVC definitions) match
the parameters required by the WAN connection.
-
Step 5 Use a serial analyzer to check the hardware at both
ends of the link and to determine whether the SABMs are being responded
to with unnumbered acknowledge (UA) packets, or to examine any other anomalous
protocol event.
-
Step 6 If the analyzer cannot identify any external problems,
check the router hardware.
-
Step 7 Swap faulty equipment as necessary.
WAN and Serial Line Connectivity Symptoms
The symptom modules in this section pertain to serial and WAN problems.
Unless otherwise indicated, each module is presented as a set of general
problems applying to all WAN types (such as X.25, point-to-point serial,
SMDS, and Frame Relay). Any special considerations for a specific network
type are noted.
WAN connectivity symptoms are discussed in the following sections:
Intermittent WAN Connectivity
Symptom: Connections can be made between some nodes, while other
nodes cannot connect. Table
12-1 outlines possible causes and suggested actions when intermittent
connectivity in serial and WAN interconnections is experienced.
Table 12-1 WAN: Intermittent WAN Connectivity
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Possible Causes Suggested Action
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Faulty interface card or cable Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial and show controllers EXEC
commands to check the status of the interface.
Step 2 Look for a line down condition and version level.
Step 3 Upgrade microcode (firmware) if the current code is older than
Version 1.7.
Step 4 Swap any nonoperational cards or cables.
CSU/DSUfailure Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to check for
input errors.
Step 2 Replace the modem.
Step 3 Observe behavior after the modem is changed.
Timing problem Step 1 Check the CSU/DSU configuration to verify that
SCTE/Terminal timing is enabled; enable serial clock transmit
external (SCTE)/terminal timing if it is not already enabled.
Step 2 If the CSU/DSU is properly configured, or if intermittent
connectivity persists after enabling SCTE/Terminal timing on
the CSU/DSU, verify that the correct network entity is
generating the system clock; reconfigure nodes and modems if
clocking is not properly configured.
Step 3 If intermittent problems persist, check cable length; if the cable
is longer than 25 feet (7.62 meters), you might need to invert the
clock on the MCI/SCI.
Step 4 Invert the data on the DSU/CSU on both ends of the connection.
Step 5 Lower the line speed to 56 KB or derivative of that speed.
Step 6 Check for possible routing loops, or misconfigurations of
routing protocols.
Network generating invalid PRs (X.25) Step 1 Verify that the interface default flow control values match the
values defined for the switch.
Step 2 Run diagnostics at the switch.
Step 3 Swap switch hardware if necessary.
Router generating invalid PRs (X.25) Step 1 Verify that the interface default flow control values match the
values defined for the WAN connection.
Step 2 Enable the debug x25 events EXEC command and examine the
cause and diagnostic codes. For more information, see the "X.25
Cause and Diagnostic Codes" appendix in the Debug Command
Reference manual.
Serial line congestion Step 1 Adjust the hold queue.
Step 2 Tune buffer sizes. For more information, see the section
"Adjusting Buffers to Ease Overutilized Serial Links" in the
"Troubleshooting Serial Line Problems" chapter.
Step 3 Apply a priority list.
Step 4 Reduce broadcast traffic.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WAN Connections Fail as Load Increases
Symptom: Users continually complain about lost connections at peak
periods. One example of this problem is in an environment that features
bridged DEC local-area transport (LAT) traffic and multiple routed protocols.
Data entry input from users (or other application requests) might be getting
buffered at the end of an already long input queue; eventually one end
of the connection times out. Table
12-2 outlines possible causes and suggested actions when WAN connections
fail as load increases.
Table 12-2 WAN: Connections Fail as Load Increases

---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Possible Causes Suggested Actions
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Noisy serial line Step 1 Determine whether input errors are increasing.
Step 2 If input errors appear, diagnose the serial line as described in the
section "Special Serial Line Tests" in the "Troubleshooting
Serial Line Problems" chapter.
Overutilized serial line Step 1 If input errors do not appear, there is a congestion problem.
Step 2 Increase the bandwidth.
Step 3 Include an appropriate priority queuing configuration statement.
Step 4 Tune buffer sizes. For more information, see the section
"Adjusting Buffers to Ease Overutilized Serial Links" in the
"Troubleshooting Serial Line Problems" chapter.
Step 5 Reduce unnecessary broadcast traffic.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WAN Connections Fail at a Particular Time of Day
Symptom: This symptom is generally an example of connections dying
under load. In this case, traffic on a serial link approaches saturation
at specific times during the day: for instance, around 8:30 a.m., noon,
and 5:30 p.m. The result is a lost connections or an inability to make
connections. Table
12-3 outlines possible causes and suggested actions when connections
fail at a particular time of day.
Table 12-3 WAN: Connections Fail at a Particular
Time of Day

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Possible Causes Suggested Action
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Overutilized bandwidth Step 1 Check the applications that are being run. Look for very large
file transfers scheduled at particular times of the day.
Step 2 If you find large file transfers that are scheduled for the time of
day at which saturation occurs, set up a priority queue based on
packet size to allow higher amounts of small-packet traffic. (The
protocol must support flow control.)
Step 3 Rearrange the timing of file transfers so that links are not
overused during normal business hours.
Step 4 Add bandwidth and consider dial backup over the new link for
applications that are taking excessive bandwidth on existing
links.
Unshielded cable runs are too close to Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to look for
electromagnetic interference (EMI) input errors.
sources Step 2 If loading is not the problem, and input errors are being
registered, inspect cable runs for proximity to EMI sources.
Step 3 Relocate or shield cables if they are found to be near EMI
sources.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Connections Fail after a Period of Normal Operation
Symptom: Connections suddenly fail and cannot be restored after
relatively normal, error-free operation. Table
12-4 outlines possible causes and suggested actions when connections
fail suddenly after a period of normal operation.
Table 12-4 WAN: Connections Fail after Normal
Operation

-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Possible Causes Suggested Action
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Hardware failure somewhere in the serial Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
link whether the link is down.
Step 2 If the link is down, refer to the section "CSU and DSU
Loopback Tests" in the "Troubleshooting Serial Line Problems"
chapter or use a serial analyzer to troubleshoot the failure.
Routing tables are incorrect Step 1 If the link is up, use the appropriate show protocol route EXEC
command.
Step 2 Determine whether routes are correct; if not, look for the source
of bad routes, such as a flapping link, a backdoor bridge between
the routed segments, or an incorrect configuration of route
redistribution between routing protocols.
Buffer misses or other software problem Step 1 If the routing table is correct and the link is up, use the
show buffers EXEC command to evaluate buffer status.
Step 2 Refer to the section "Adjusting Buffers to Ease Overutilized
Serial Links," in the "Troubleshooting Serial Line Problems"
chapter. Modify buffers as necessary to prevent dropped
connections.
Step 3 Contact your technical support representative if all actions fail to
resolve the problem.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WAN Users Cannot Connect to Resources over a New
HDLC Link
Symptom: Traffic does not pass through a newly installed router
interconnecting broadcast networks via a High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC)
point-to-point link. Table
12-5 outlines possible causes and suggested actions when users cannot
connect to resources over a new HDLC link.
Table 12-5 WAN: Users Cannot Connect to Resources
over a New HDLC Link

---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Possible Causes Suggested Action
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Link is down Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
whether the link is down.
Step 2 If the link is down, refer to the "CSU and DSU Loopback Tests"
section in the "Troubleshooting Serial Line Problems" chapter
or use a serial analyzer to troubleshoot the failure.
Keepalive packets not being received Step 1 Use the debug serial interface privileged EXEC command to
determine the status of keepalive packets.
Step 2 If keepalive packets are not incrementing, refer to the section
"CSU and DSU Loopback Tests" in the "Troubleshooting Serial
Line Problems" chapter.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WAN Users Cannot Connect to Resources over a New
X.25 WAN Link
Symptom: Traffic does not pass through a newly installed router
interconnecting broadcast networks via an X.25 WAN. Look for problems associated
with the new installation, especially when LANs previously interconnected
via the WAN continue to communicate with no disruption of service. Table
12-6 outlines possible causes and suggested actions when users cannot
connect to resources over a new X.25 link.
Note The process of problem isolation for Defense Data
Network (DDN) X.25 networks is essentially the same, except for the DDN-defined
dynamic mapping capability.
Table 12-6 WAN: Users Cannot Connect to Resources
over New X.25 WAN Link

------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Possible Causes Suggested Actions
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Link is down Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
whether the link is down.
Step 2 If the link is down, refer to the "CSU and DSU Loopback Tests"
section in the "Troubleshooting Serial Line Problems" chapter.
Switch is misconfigured Step 1 Check the configuration of the switch; look for bad address
specifications, incorrect VC parameter settings, or other
configuration errors.
Step 2 If you find errors, modify the configuration and use the
show interfaces serial EXEC command to check the status of
the line.
Misconfigured router, incorrect cabling, or Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
bad router hardware the status of the interface. If the interface is up, but the line
protocol is down, check the Link Access Procedure, Balanced
(LAPB) state.
Step 2 If the LAPB state is not CONNECT, attach a serial analyzer.
Step 3 Use the serial analyzer to look for UA packets sent in reply to
SABMs.
If UAs are not being sent, one of the possible causes described
in this table is the likely problem.
Step 4 Reconfigure equipment or replace equipment as required.
Step 5 If the show interfaces serial EXEC command indicates that the
interface and line protocol are up, but no connections can be
made, use the write terminal privileged EXEC command to
check the router configuration.
Step 6 Look for x25 map interface configuration commands and ensure
that the correct addresses are specified.
Step 7 If dynamic routing is being used in the network, verify that the
broadcast keyword is included in the x25 map command.
Step 8 Ensure that all router configuration options match switch
settings.
Step 9 Modify router configuration as needed to resume operation.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
WAN Users Cannot Connect to Resources over a New
Frame Relay Link
Symptom: Traffic does not pass through a newly installed router
interconnecting broadcast networks via a Frame Relay WAN. Look for problems
associated with the new installation, especially when LANs previously interconnected
via the WAN continue to communicate with no disruption of service. Table
12-7 outlines possible causes and suggested actions when users cannot
connect to resources over a new Frame Relay link.
Table 12-7 WAN: Users Cannot Connect to Resources
over New Frame Relay Link

------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Possible Causes Suggested Actions
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Frame Relay switch is misconfigured Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
(dynamic Data Link Connection Identifier the status of the line and to determine whether Local
[DLCI] and protocol address mapping) Management Interface (LMI) updates are being received.
Step 2 If LMI updates have not been received, enable the debug
frame-relay lmi privileged EXEC command; look for LMI
information to determine whether the switch and router are
sending and receiving LMI packets.
Step 3 Confirm that the DLCI numbers provided by your vendor match
the PVC output resulting from the debug frame-relay lmi
privileged EXEC command.
Step 4 Check the configuration of the Frame Relay switch; make sure
LMI matches the router.
Router is misconfigured (wrong keepalive Step 1 Use the write terminal privileged EXEC command to check for
setting) LMI keepalive setting (dynamic mode). Ten seconds is the
default (not displayed).
Step 2 Compare LMI keepalive setting with the Frame Relay switch
setting. The LMI keepalive setting should be equal to or less
than the Frame Relay switch.
Step 3 Make sure that the router speed does not match the switch,
which is normally set 2--5 seconds slower than the router.
Misconfigured access list Step 1 Evaluate access lists at both ends of the connection.
Step 2 Make sure there are no inadvertent access denials.
Step 3 Modify access lists as needed or remove to test connectivity.
Cabling problem Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
the status of the interface.
Step 2 Check cabling. Refer to the "Developing a Strategy for Isolating
Problems" section in the "Troubleshooting Overview" chapter.
Step 3 Replace any incorrectly configured or failed cables.
Failed hardware Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial command to determine the status
of the interface.
Frame Relay does not support Loop Back, but if Local DSU is
placed into Local Loopback, the input packets will equal output
packets. These packets are the LMI updates the router sends out.
Step 2 Replace hardware as necessary.
Router is misconfigured (dynamic DLCI Step 1 Check the output of the show interface serial EXEC command
and protocol address mapping) to determine the status of the interface.
Step 2 Determine whether DLCI-to-protocol mapping is dynamic or
static; set to the correct mode if it is not correct.
Step 3 If dynamic mapping is implemented and if the interface and line
protocol are up, but no connections can be made, examine the
output of the show frame-relay map EXEC command.
Step 4 Determine whether any of the far end networks have been
learned by the local router.
Step 5 If far end networks have been learned and if the protocol
supports ping, ping the nearest interface of the remote router to
verify that you can reach that point.
Step 6 If the interface and line protocol are up, and you cannot ping, the
Frame Relay network is probably misconfigured.
Step 7 If you can ping, ping through to the other side of the router,
working out to end stations.
Step 8 Reconfigure equipment as necessary. (At the router, be sure that
the remote DLCI number is mapped to the protocol address at
the far end.)
Step 9 If the output of the show frame-relay map EXEC command
indicates that no far end networks have been learned, enable the
debug framerelay events EXEC command and run the
appropriate show route EXEC command.
Step 10 Identify the exchanges that are occurring between the router and
the switch and determine whether any routing protocol
information is being learned.
Step 11 Change the router configuration as necessary.
Router is misconfigured (static Frame Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
Relay address mapping) the status of the interface.
Step 2 Determine whether DLCI-to-protocol mapping is dynamic or
static; set to correct mode if not correct.
Step 3 If the interface and line protocol are up and if static mapping is
implemented, but no connections can be made, examine the
output of the show frame-relay map EXEC command.
Step 4 The status should be active. If not, compare the configurations
on the switch and the router and make sure they match.
Step 5 If the show frame-relay map EXEC command indicates that
the status is active, examine the output of the show route EXEC
command for the appropriate protocol to determine whether
routing information is accumulating. Misconfigured access lists
might be a cause.
Step 6 Make sure BROADCAST tag is set on your map statements if
your are running a routing protocol.
Step 7 Double-check that the NETWORK ADDRESS and DLCI are set
correctly in your configuration.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Note You cannot ping the local router's frame-relay
interface unless a static map is configured to permit this action.
WAN Users Cannot Connect to Resources over a New
SMDS Link
Symptom: No traffic of any kind is passing through a newly installed
router interconnecting broadcast networks via an SMDS WAN link. Look for
problems associated with the new installation, especially when LANs previously
interconnected via the WAN continue to communicate without disrupted service.
If you are having difficulty establishing connections over an SMDS cloud,
obtain the following information as a preliminary step before beginning
the problem isolation process:
-
Use the show arp EXEC command to determine whether any SMDS devices
were detected on the switch.
-
Use the debug serial interface privileged EXEC command to determine
whether packets are being sent and received.
-
Use the debug serial packet privileged EXEC command to obtain the
entire SMDS header and payload data when SMDS packets are transmitted or
received on an interface.
-
Use the debug arp privileged EXEC command to determine other SMDS
devices that are being detected on the switch.
-
Use the show smds traffic EXEC to verify errors and packets transmitted
and received.
Table 12-8
outlines possible causes and suggested actions when users cannot connect
to resources over a new SMDS link.
Table 12-8 WAN: Users Cannot Connect to Resources
over New SMDS Link

-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Possible Causes Suggested Actions
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SMDS switch is misconfigured Step 1 Check the router and switch configurations for an address
mismatch.
Step 2 Make sure that the SMDS switch is configured for multicast or
static mapping (depending on the intended network setup).
Router misconfigured (general SMDS) Step 1 Use the write terminal privileged EXEC command to evaluate
the configuration of the router.
Step 2 Compare the configuration with requirements for the switch.
Look for bad address specifications, an incorrect mode
specification (multicast versus static), or a missing
encapsulation smds interface configuration command.
Step 3 Modify the configuration as necessary to make the router match
SMDS network requirements. Verify that SMDS DXI is enabled
or disabled as required by the SDSU.
In Cisco IOS Release 10.0 and later, SMDS DXI is enabled by
default.
Misconfigured SMDS interface or Step 1 Use the show arp EXEC command to determine what other
multicast addresses devices, if any, have been detected on the switch.
Step 2 If none have been detected, make sure that the SMDS address
specified in the smds address interface configuration command
matches the address of the attached switch.
Step 3 Make sure that the SMDS multicast addresses specified in the
smds multicast interface configuration command match the
addresses configured on the switch.
Step 4 Make sure that the smds enable-arp interface configuration
command is present so that higher layers learn about the router.
Step 5 Check the static maps configured on the router. To allow the
SMDS software to translate a destination address into a proper
SMDS address for outgoing packets, make sure that static maps
are configured for all nonlearning protocols.
Step 6 If SMDS data is still not being received, even when packets are
being sent, check all connections for physical connectivity.
Step 7 If the physical connections are operational, and packets still are
not being received, check the SDSU configuration.
Router misconfigured (static SMDS Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
address mapping) the status of the interface.
Step 2 Use the show smds map EXEC command to determine whether
the mapping mode is multicast or static; reconfigure the mode if
it is incorrect.
All network protocols, with the exception of IP and ISO
Connectionless Network Service (CLNS), require static
mapping from protocol addresses to SMDS addresses.
Step 3 If IP or ISO CLNS is being routed, check the multicast group
specification. Make any necessary address changes.
Step 4 If static mapping is implemented, if the interface and line
protocol are up, and if connections cannot be made, enable the
debug serial interface privileged EXEC command.
Step 5 Based on the debug output, determine whether the correct
destination address is being used.
Step 6 Make configuration changes as necessary to the mapping, mode,
or encapsulation specification.
Misconfigured access list Step 1 See Table 12-7 for suggested actions.
Cabling problem Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
the status of the interface.
Step 2 Check cabling. Refer to the sections "Using the show interfaces
Command to Troubleshoot Serial Lines" and "Special Serial
Line Tests" in the "Troubleshooting Serial Line Problems"
chapter.
Step 3 Replace any incorrectly configured or failed cables.
Failed hardware Step 1 Use the show interfaces serial EXEC command to determine
the status of the interface. To isolate specific problem
equipment, perform loopback and ping tests as described in the
section "CSU and DSU Loopback Tests," and "Using Extended
ping Tests to Troubleshoot Serial Lines" in the "Troubleshooting
Serial Line Problems" chapter.
Step 2 Replace hardware as necessary.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Some Users Cannot Connect to Resources over a WAN
Symptom: Some users or applications are able to reach resources
over a serial/WAN link through a router while other users cannot. Table
12-9 outlines possible causes and suggested actions when some users
cannot connect to resources over a WAN.
Table 12-9 WAN: Some Users Cannot Connect
to Resources over WAN

-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Possible Causes Suggested Actions
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Misconfigured access list Step 1 See Table 12-7 for suggested actions.
Host configuration is not set up to send Step 1 Verify that the host is configurated to send ARPs.
ARPs Step 2 Modify as necessary.
Host configuration points at wrong router Step 1 Check host configuration for default gateway specification.
Step 2 Modify host configuration as necessary.
Discontinuous subnet addressing (IP) Step 1 Check the network configuration for discontinuous network
address space assignment.
Step 2 If you find discontinuous network address space assignments,
use secondary IP addresses to accommodate physical
discontinuity.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------







Copyright 1988-1995
© Cisco Systems Inc.
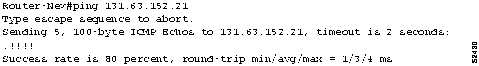 Figure
12-11 and Figure
12-12 illustrate the effect of the ping exchange on the ARP cache of
Router-New (after the clear arp-cache command was executed).
Figure 12-11
illustrates that before the ping transmission, the ARP cache does not include
the target host. After the ping, the ARP entry for the host is included
in the ARP cache for Router-New. (See Figure
12-12.)
Figure
12-11 and Figure
12-12 illustrate the effect of the ping exchange on the ARP cache of
Router-New (after the clear arp-cache command was executed).
Figure 12-11
illustrates that before the ping transmission, the ARP cache does not include
the target host. After the ping, the ARP entry for the host is included
in the ARP cache for Router-New. (See Figure
12-12.)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()